Why use o3-pro?
Unlike general-purpose models like GPT-4o that prioritize speed, broad knowledge, and making users feel good about themselves, o3-pro uses a chain-of-thought simulated reasoning process to devote more output tokens toward working through complex problems, making it generally better for technical challenges that require deeper analysis. But it’s still not perfect.
Measuring so-called “reasoning” capability is tricky since benchmarks can be easy to game by cherry-picking or training data contamination, but OpenAI reports that o3-pro is popular among testers, at least. “In expert evaluations, reviewers consistently prefer o3-pro over o3 in every tested category and especially in key domains like science, education, programming, business, and writing help,” writes OpenAI in its release notes. “Reviewers also rated o3-pro consistently higher for clarity, comprehensiveness, instruction-following, and accuracy.”
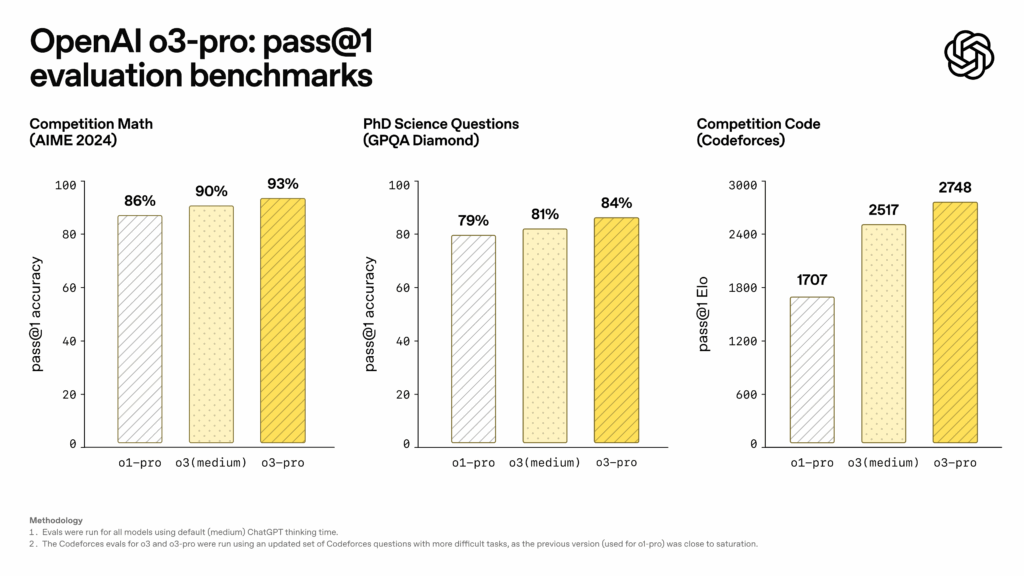
OpenAI shared benchmark results showing o3-pro’s reported performance improvements. On the AIME 2024 mathematics competition, o3-pro achieved 93 percent pass@1 accuracy, compared to 90 percent for o3 (medium) and 86 percent for o1-pro. The model reached 84 percent on PhD-level science questions from GPQA Diamond, up from 81 percent for o3 (medium) and 79 percent for o1-pro. For programming tasks measured by Codeforces, o3-pro achieved an Elo rating of 2748, surpassing o3 (medium) at 2517 and o1-pro at 1707.
When reasoning is simulated

It’s easy for laypeople to be thrown off by the anthropomorphic claims of “reasoning” in AI models. In this case, as with the borrowed anthropomorphic term “hallucinations,” “reasoning” has become a term of art in the AI industry that basically means “devoting more compute time to solving a problem.” It does not necessarily mean the AI models systematically apply logic or possess the ability to construct solutions to truly novel problems. This is why Ars Technica continues to use the term “simulated reasoning” (SR) to describe these models. They are simulating a human-style reasoning process that does not necessarily produce the same results as human reasoning when faced with novel challenges.

